I. Rehabilitation of spinal cord injury
(1) Rehabilitation treatment
1. Acute phase. Within 8 weeks after spinal cord injury, all patients were bedridden, especially those with spinal fracture, which needed to be bedridden for 6-12 weeks. For spinal cord injury caused by other reasons, the bedridden time was very short.
2. Early recovery period. This period continues some training in the acute phase, such as vascular conditioning training, muscle strengthening training, passive movement of the affected limb, etc.
3. Mid-recovery. Because of spasm, it is still difficult to move freely. In addition to the treatment of spasm, standing and walking training should be carried out, which is especially important for patients with low imperfection impairment.
4. Late recovery. The patient's function has recovered to some extent in many aspects, and wheelchair training, standing, walking in parallel bars and walking with crutches are still needed to improve the self-care ability of daily life.
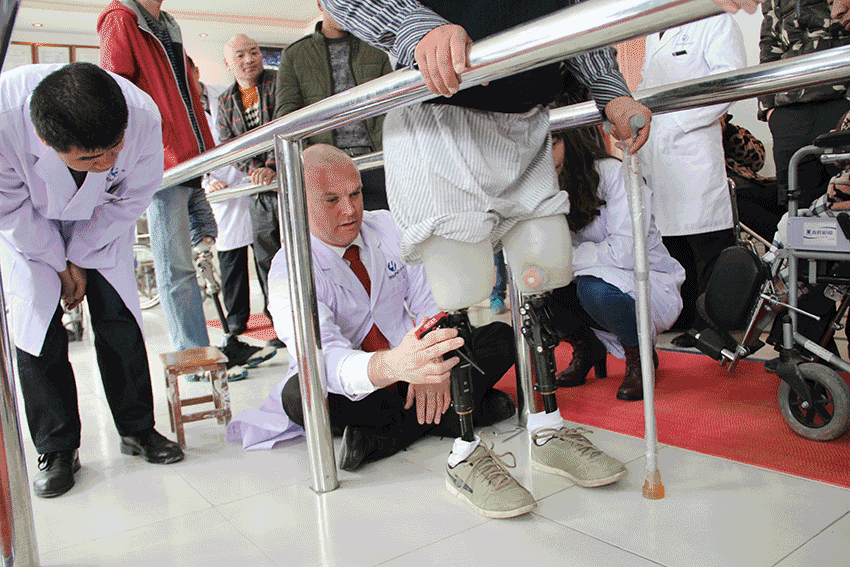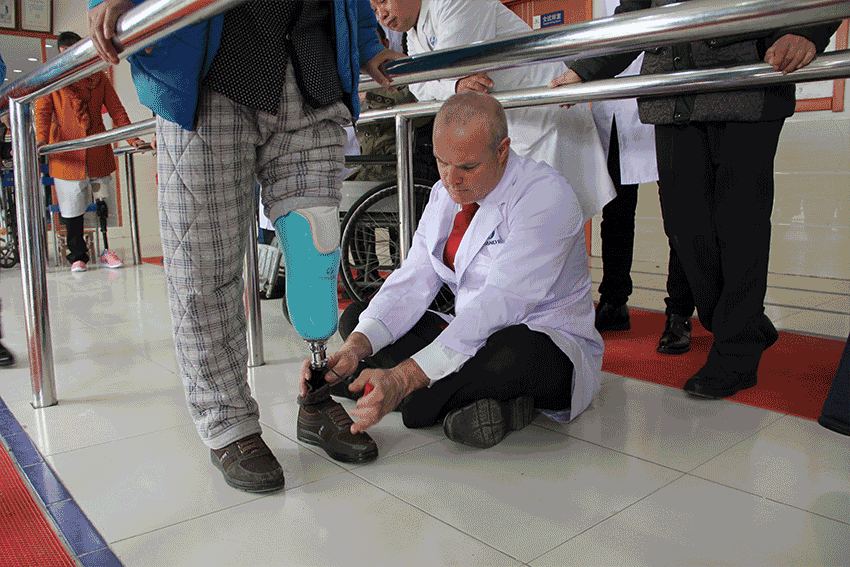
II. Rehabilitation after amputation
Key points of rehabilitation treatment after amputation
1. Observation points: Whether amputee patients are suitable for prosthesis is mainly observed from four aspects: cardiovascular function, central nervous system, vision, muscle strength and joint range of motion.
2. Psychological nursing.
3. Rehabilitation training.
4. Family rehabilitation guidance.
(1) Maintain an appropriate weight.
(2) Prevent muscle atrophy of stump.
(3) Prevent residual limb swelling into fat deposition.
(4) Keep the skin of the stump and the prosthesis receiving cavity clean.
(5) Rehabilitation of phantom limb pain.
III. The rehabilitation of hemiplegia
(1) Rehabilitation treatment
1. Reasonable position of the patient's bed in the ward.
2. Keep the chair and wheelchair sitting properly.
3. The purpose of acute treatment is to cooperate with the rescue treatment of clinicians, prevent joint contracture, shoulder subluxation, bedsore, pneumonia, and so on, and create conditions for further rehabilitation training.
4. Muscle massage.
5. Early bed activities: bed turning over training, bed bridge movement, bed sitting up.
6. Maintain the range of motion of the joint training: general training 2 times a day, 10 to 20 minutes each time.
(2) Rehabilitation during convalescence
1. Sitting training: mainly sitting balance training.
2. Walking training: mainly walking training in parallel bars.
3. Training under supine position: training to suppress the spasm of lower limb extensor muscle.
(3) Training for sequelae period
1. Use of wheelchairs.
2. Use of walking sticks and walkers.
3. Ability training of daily living activities (changing clothes, eating, bathing and transferring).
4. Orthotics.
IV. Rehabilitation of osteoarthritis
(1) Proper rest.
(2) Exercise therapy.
(3) Physical therapy and acupuncture.
(4) Take medicine and inject drugs into the joint.
(5) Use of orthopaedic devices, crutches and other instruments, operations, etc.
V, the rehabilitation of cerebral palsy in children
Basically diagnosed children to early intervention, early rehabilitation treatment. Rehabilitation includes medical rehabilitation, educational rehabilitation (guided and special education), social rehabilitation and vocational rehabilitation. Medical rehabilitation includes exercise therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture and massage, physical therapy, music therapy, sensory integration therapy, and orthotic correction.
USA YOBAND prosthetic innovation technology is shared, focusing on financial and material resources, focusing on and producing its own research and development, giving full play to its unique core competitive advantages, and fully integrating global resources with international peers for the benefit of disabled friends! So when selecting a prosthetic company, the amputee who installs prosthetic limbs must investigate on the spot to determine whether the prosthetic company really has a technical team to make a prosthetic receptor cavity. The qualified prosthetic receptor cavity plays a key role in their own comfortable experience and prosthetic walking gait.