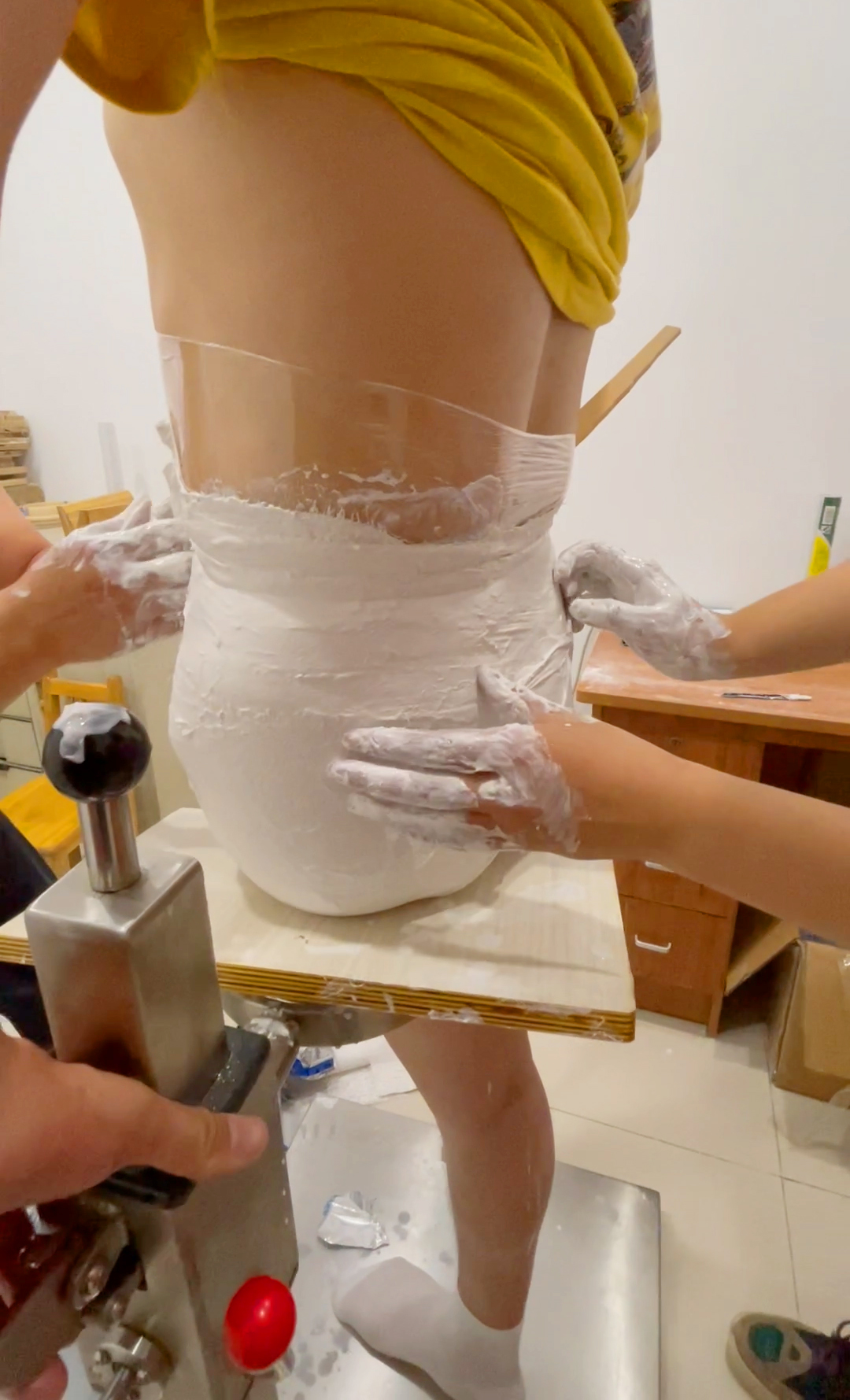
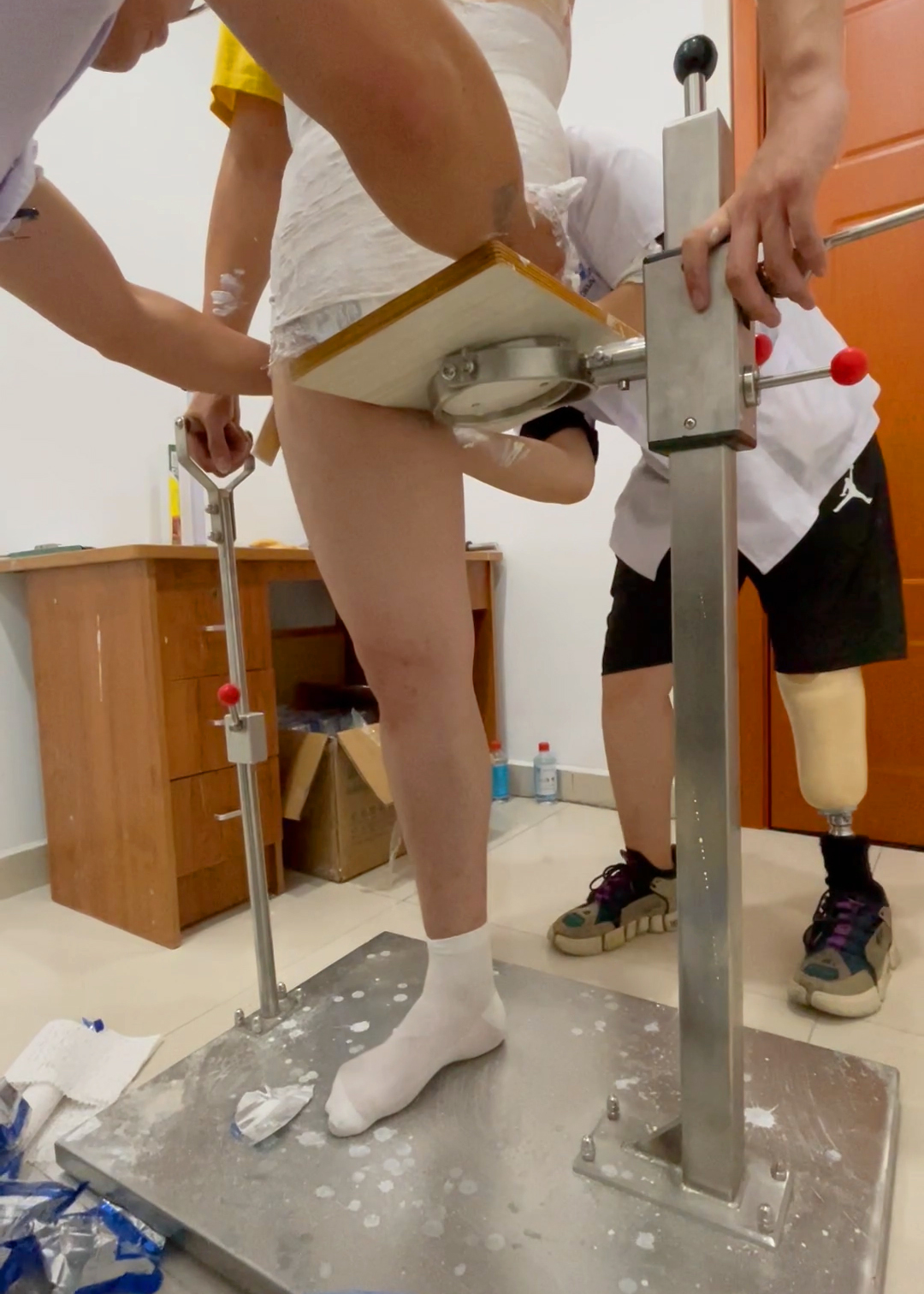
Hip amputation is the surgical removal of a disabled lower limb to save a patient's life. Wheelchair mobility is the simplest solution for lower extremity amputees. By driving the wheelchair, hip amputees can expand their range of motion. Fitted with a prosthesis or other device, hip amputees can be trained to regain the ability to stand and even walk.
The hip amputation prosthesis consists of two prostheses which contain the pelvis, the receiver cavity of the stump and are connected with the receiver cavity. Hip amputation prosthesis is suitable for amputation of hip joint, subtrochanteric amputation, subtrochanteric amputation of one side hip joint, congenital lower limb loss, total pelvis resection and so on.
The prosthetic socket should meet the following requirements when it is designed and manufactured.
① It is convenient to put on and take off, comfortable to wear and beautiful to look as much as possible.
② The prosthetic socket is in full contact with the soft tissue of the pelvis and the residual end stump, so as to increase the force area and even load bearing as far as possible.
③ Bone protrusion, damage and severe scar should be exempted.
④ The influence of residual limb volume changes should be considered. The recipient cavity should be adjustable to accommodate weight gain or loss and changes in residual volume as the patient is placed in different body positions.
The shape of the iliac crest should be well molded to avoid rotation of the stump in the prosthetic socket.
In order to facilitate urine and feces care, in the middle opening below the front of the receiving cavity, some patients should consider the exit of colostomy and catheter.
Consider heat dissipation and air permeability.
(8) When the prosthetic socket is on the line, a certain forward Angle is beneficial to increase the stability of the upright position. The Angle is based on the patient's comfort and balance.
Selection of components for Canadian hip amputation prostheses
The earliest hip release prostheses were shell prostheses, and the most common form is the Canadian one. The hip joint hinge is installed in the front and lower part of the receiving cavity, which is uniaxial without locking joint. Therefore, the hip joint flexion Angle control device is installed at the bottom of the receiving cavity, such as the flexion control belt, which has the function of assisting the extension of the hip joint. In this way, the hip axis is fixed and alignment is difficult. Later Northwettons were fitted with an adjustment mechanism for easy alignment, and the joint had a built-in stride control that limited the Angle of flexion. The knee joint uses shell hinge assembly. The receiving cavity of the endoskeletal hip disconnection prosthesis still adopts The Canadian type, and the hip and knee joints adopt the standard component structure, which is easy to adjust the line, stable, light in weight and good in appearance. As the number of joint types increases, the choice of components for hip amputation prostheses has become diversified. Hip joint can choose free flexion without lock, can also choose with manual lock, only when sitting open joint flexion; Knee joint can choose support period control, manual lock, free knee joint. After training, some patients can swing to walk or swing to walk with forearm crutch or walker. Patients can also perform a four-point gait using crutches or a walker, lifting the torso with the hands and then flexing and rotating the pelvis to complete the initial swing. This four-point gait consumes a lot of energy and is slow. Child amputees are light and have a low center of gravity, and some can move without crutches.
Prosthesis height and alignment
Due to the loss of lower limbs, the position of the center of gravity of hip amputees has changed greatly compared with normal people. After the prosthesis is installed, the center of gravity needs to be adjusted to establish a new balance. Therefore, hip amputation prosthesis generally starts with short post prosthesis to adapt to the balance between standing and walking. After a period of acclimatization of standing balance and stepping training with the aid of walking aid, the prosthesis is gradually raised. The final height of the prosthesis depends on the patient's height before amputation and the stability and aesthetics of walking with the prosthesis. The height of a normal person is approximately equal to the distance between the middle fingers of both hands when the arms are flat and extended. In order to increase the stability of standing and walking, or to easily achieve the conversion from sitting position to standing position, under the premise of not affecting body symmetry and beautiful gait, the leg part or leg part of the prosthesis is generally shortened a few centimeters. Pediatric hip amputation prosthesis height is often set according to the normal child altimeter and adjusted as age increases.
The alignment of the prosthesis follows the alignment principle of Canadian prosthesis: static alignment, sagittal plane, bearing line through the hip joint behind, knee joint in front, front of the ankle joint, dynamic alignment on the basis of fine tuning; On the coronal plane, the height of the mechanical axis of the hip, knee and ankle joints of the left and right lower limbs above the ground must be symmetrical with respect to the center line of the body.
Interactive gait walking prosthesis
Because swinging or swinging to walk requires the upper limbs to lift the weight of the body and the prosthesis, and to swing the foot forward simultaneously off the ground, it is difficult for amputees with relatively weak upper limb strength. The search began for walking patterns that more closely resembled natural gait for hip amputees. Some paraplegics wear orthotics and can achieve an interactive gait, or four-point gait, with the help of crutches or walking frames. Some people have applied the principle of interactive walking of these orthopaedic devices to the design of hip amputee prostheses, enabling hip amputees to walk with interactive gait, look more like normal people, and reduce the energy consumption of walking.
In 1984, the university of Louisiana at alternating stepped orthoses (LouisanaStateUniversityReciprocatingGaitOrthosis, strop RGO) appear soon, It has been reported that a child with severe congenital limb deformity after lower limb amputation was fitted with an interactive gait prosthesis using RGO and shell hip amputation prosthesis. The design is a combination of a modified Canadian hip and a RGO joint on each leg. An axis is used to connect their centers, so that the interactive joint on the side is consistent with the center of the Canadian hip joint in the middle, and the interactive movement is transmitted through the ring lock and the interactive joint, driving the Canadian hip joint and the prosthetic leg to move, so as to realize the interactive gait.
In 1990, based on the principle of ORLAU interactive walking orthosis, an interactive walking prosthesis system was designed for a child with congenital complete lower limb absence. The advantage of this design is that the prosthesis has good lateral stability in the single support period, while the disadvantage is that the weight of the mechanism is large and the lower limbs only rely on the universal gravitation to drive the pendulum movement to complete the swinging period.
In 2001, an interactive walking prosthesis was designed and fitted to a hip amputee using the advanced alternating stepping orthotic principle. It has a modified prosthetic hip mounted in front of the receiving cavity near the side. The two hips are connected by an ARGO guide cable located behind the receiving cavity. A hip lock is installed on each joint. When the bilateral hip lock is in the lock position, the patient can walk through the prosthesis with the guide cable. When the bilateral hip lock is unlocked, the patient can switch from standing position to sitting position. These designs are characterized by knee and ankle joint fixation. The interactive motion device of the paraplegic orthosis is combined with the modified hip joint of the hip joint amputation prosthesis on the sagittal plane to achieve the interactive motion of the prosthetic leg. When patients put on prosthetics, with the help of crutches or walkers, after training, they can walk with interactive gait, reduce the load of the upper limbs, better safety, more natural gait, easier to be accepted.
Summary: The number of hip amputees due to trauma, war, disease and other causes is increasing. With the improvement of medical technology and nursing conditions, the survival rate and life expectancy of hip amputees have increased. In order to improve their appearance, quality of life, psychology and return to society, these patients can stand, swing or walk by installing Canadian hip amputation prosthesis, and can walk with interactive gait by combining prosthesis technology and orthosis technology. The interactive gait prosthesis can reduce the load of upper limbs, reduce the energy consumption of walking, and the gait pattern is closer to normal people. The further research of interactive gait prosthesis is very valuable for the development of hip amputation prosthesis.
Part of the content is extracted from [Chinese Rehabilitation Theory and Practice]