Orthosis is a kind of external appliance used to correct deformities of limbs and trunk or bone and joint diseases, neuromuscular atrophy or diseases. It is assembled outside the human body and used to improve the human nerve, muscle or bone structure and compensate its function. The purpose is to replace the missing muscle by external force, prevent and correct deformity, make up for the lack of muscle strength, protect the painful part, preoperative and postoperative fixation, so as to promote functional recovery. Those used for the torso and limbs were called braces, and those used for the limbs were called splints. The orthosis is effective, reliable, durable, safe to use, easy to adjust and easy to be accepted by patients. Orthoses are used for treatment in addition to compensation of function. Modern rehabilitation medicine has regarded orthosis technology as four major rehabilitation techniques for hemiplegia as important as physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech therapy.
I. The basic function of orthoses
1. Steady support
By restricting the joint with abnormal movement or abnormal range of motion, the joint can be stabilized, pain can be alleviated, and weight bearing function can be improved.
For example, orthotics for neuromuscular paralysis of the lower extremities can help stabilize the joint.
2. Fixation and protection
To promote healing by immobilization of a diseased limb or trunk.
3. Prevent or correct deformity
Through the resistance of the orthosis, the correction of bone and joint deformities caused by abnormal bone development or external force.
Such as the correction of abnormal growth and development of children.
4. Lighten the load
The orthosis is used to share the weight of the long axis of the limbs or trunk bones and joints. Such as hemiplegic patients for the healthy side to share the weight of the leg in affected side.
5. Compensation function
Power orthoses can compensate weak muscles and promote limb movement through power devices. Such as electric wheelchair can compensate for the lack of upper limb strength to drive the wheelchair.
6. Boost your confidence
Orthoses correct malformations, improve patients' activities of daily living, thereby reducing patients' psychological burden and promoting
Rehabilitation, to promote and restore the patient's self-confidence.
7. For the treatment of hemiplegic patients
The use of lower limb orthosis in the early rehabilitation of hemiplegic patients can be used to prevent the occurrence of disuse and misuse syndrome and promote the early rehabilitation of motor function and ADL (activities of daily living).
II. Classification of orthoses
1. Upper limb orthoses
Upper limb orthoses include hand orthoses (HO), wrist orthoses (WHO), elbow, wrist and hand orthoses (EWHO),
Shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand orthoses (SEWHO). Upper limb orthoses are used primarily to protect paralyzed muscles against antagonists
Spasm plays a role in supporting and correcting the deformity of the joint.
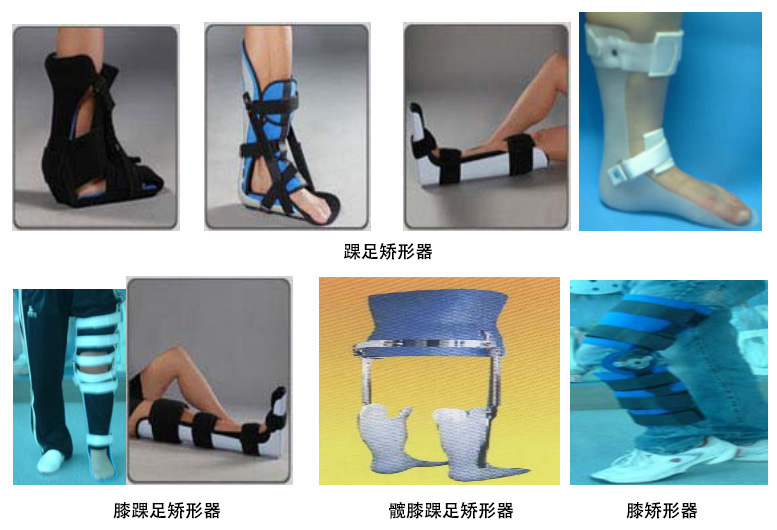
2. Lower limb orthoses
Lower limb orthoses include ankle and foot orthoses (AFO), knee and ankle orthoses (KAFO), knee orthoses (KO), hip, knee, ankle and foot orthoses (HKAFO) foot orthoses (FO). The functions of lower extremity orthoses are to fix unstable joints, compensate for paralyzed muscles, reduce the weight bearing of the affected limb, correct deformity, compensate for limb defects and involuntary motor control. At present, in the rehabilitation of hemiplegic patients, the use of lower limb orthoses has been proposed as "therapeutic" orthoses to prevent the occurrence of disuse and misuse syndrome in hemiplegic patients, and promote the recovery of motor function and ADL ability. The objectives of lower extremity orthoses are to fix unstable joints, promote early ambulation, correct abnormal walking patterns, and prevent and correct deformities.
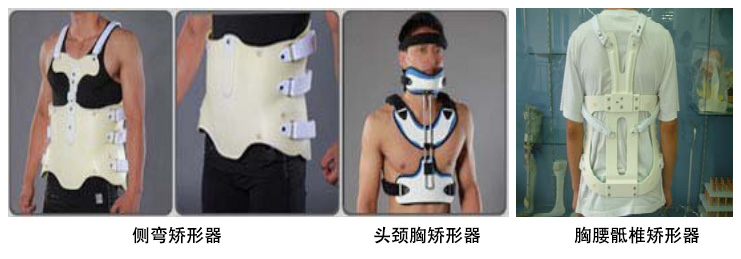
3. Spinal orthoses
Spinal orthoses include scoliosis orthoses, cervical orthoses, soft thoracolumbar orthoses, and rigid thoracolumbar orthoses, etc. Its role is to limit the movement of the spine, prevent and correct spinal deformity, reduce pain, reduce weight bearing of vertebrae, maintain the stability of the spine, protect paralyzed muscles and other functions.